Browse Articles
Conditioning Medicine
International bi-monthly journal of cell signaling, tissue protection, and translational research.
Current Location:Home / Browse Articles
Mitochondrial shaping proteins as novel treatment targets for cardiomyopathies
Time:2020-09-17
Number:11501
Siavash Beikoghli Kalkhoran1,2,3, Sauri Hernandez-Resendiz2,3,4, Sang-Ging Ong5,6, Chrishan J.A. Ramachandra2,3, Derek J. Hausenloy1,2,3,7,8
Author Affiliations


- 1The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute, Institute of Cardiovascular Science, University College London, UK.
- 2Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disorder Programme, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore.
- 3National Heart Research Institute Singapore, National Heart Centre, Singapore.
- 4Tecnologico de Monterrey, Centro de Biotecnologia-FEMSA, Nuevo Leon, Mexico.
- 5Department of Pharmacology, University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois, United States of America.
- 6Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois, United States of America.
- 7Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University Singapore, Singapore.
- 8Cardiovascular Research Center, College of Medical and Health Sciences, Asia University, Taiwan.
Conditioning Medicine 2020. 3(4): 216-226.
Abstract
Heart failure (HF) is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. The prevalence of HF continues to rise, and its outcomes are worsened by risk factors such as age, diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and ischemic heart disease. Hence, there is an unmet need to identify novel treatment targets that can prevent the development and progression of HF in order to improve patient outcomes. In this regard, cardiac mitochondria play an essential role in generating the ATP required to maintain normal cardiac contractile function. Mitochondrial dysfunction is known to contribute to the pathogenesis of a number of cardiomyopathies including those secondary to diabetes, pressure-overload left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), and doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Mitochondria continually change their shape by undergoing fusion and fission, and an imbalance in mitochondrial fusion and fission have been shown to impact on mitochondrial function, and contribute to the pathogenesis of these cardiomyopathies. In this review article, we focus on the role of mitochondrial shaping proteins as contributors to the development of three cardiomyopathies, and highlight their therapeutic potential as novel treatment targets for preventing the onset and progression of HF.
Keywords: Mitochondrial morphology, heart failure, diabetic cardiomyopathy, left ventricular hypertrophy, doxorubicin cardiotoxicity.
Abstract
Heart failure (HF) is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. The prevalence of HF continues to rise, and its outcomes are worsened by risk factors such as age, diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and ischemic heart disease. Hence, there is an unmet need to identify novel treatment targets that can prevent the development and progression of HF in order to improve patient outcomes. In this regard, cardiac mitochondria play an essential role in generating the ATP required to maintain normal cardiac contractile function. Mitochondrial dysfunction is known to contribute to the pathogenesis of a number of cardiomyopathies including those secondary to diabetes, pressure-overload left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), and doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Mitochondria continually change their shape by undergoing fusion and fission, and an imbalance in mitochondrial fusion and fission have been shown to impact on mitochondrial function, and contribute to the pathogenesis of these cardiomyopathies. In this review article, we focus on the role of mitochondrial shaping proteins as contributors to the development of three cardiomyopathies, and highlight their therapeutic potential as novel treatment targets for preventing the onset and progression of HF.
Keywords: Mitochondrial morphology, heart failure, diabetic cardiomyopathy, left ventricular hypertrophy, doxorubicin cardiotoxicity.
Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. The prevalence of HF continues to rise as the population continues to age, with an estimated 6.2 million American adults having HF between 2013 and 2016, compared with an estimated 5.7 million between 2009 and 2012 (Virani et al., 2020). The risk of developing HF is increased in the presence of certain risk factors such as diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, valvular heart disease, and doxorubicin chemotherapy, each of which can result in the development of cardiomyopathy. There is an urgent need to discover novel treatment targets that can prevent the onset and progression of HF, and improve clinical outcomes in patients with these different cardiomyopathies. In this regard, cardiac mitochondria play an essential role in providing the energy requirements needed to maintain normal cardiac contractile function. Perturbations in mitochondrial function have been shown to play a central role in the pathogenesis of a number of cardiomyopathies (Ramachandra et al., 2020). In particular, changes in mitochondrial shape, through the process of mitochondrial fusion and fission, are known to impact on cellular processes critical to normal cardiac physiology including mitochondrial respiratory function, calcium homeostasis, redox balance, mitochondrial quality control, and cell survival/death pathways (Ong et al., 2010; 2013; 2015; Hernandez-Resendiz et al., 2020). Crucially, imbalances in mitochondrial fusion and fission can impact on mitochondrial function, and predispose to the development of cardiomyopathy, positioning the mitochondrial shaping proteins as novel treatment targets for preventing HF (Kalkhoran et al., 2020). In this article, we focus on the roles that mitochondrial shaping proteins play in contributing to the pathogenesis of cardiomyopathies secondary to diabetes mellitus (DM), pressure-overload left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), and doxorubicin cardiotoxicity, and we highlight potential therapeutic strategies for preventing the onset and progression of HF in these patients.
Mitochondrial shaping proteins and the heart
Mitochondria are dynamic organelles that continually change their shape by undergoing the processes of fission and fusion to generate fragmented or elongated mitochondria, respectively (Ong et al., 2010; 2013; 2015; Hernandez-Resendiz et al., 2020). Mitochondrial fission is required for cell division, apoptosis, and selective removal of damaged mitochondria by the process of mitophagy. It is regulated by the cytosolic fission protein, dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) (Frank et al., 2001), which translocates to mitochondria, and binds to its outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) receptors, human fission protein 1 (hFis1) (James et al., 2003), mitochondrial fission factor (MFF) (Gandre-Babbe et al., 2008), and the mitochondrial dynamics proteins of 49 kDa (MiD49) and 51 kDa (MiD51) (Palmer et al., 2011; Samangouei et al., 2018), to execute scission of a single mitochondrion into two mitochondria. Mitochondrial fusion allows the replacement of damaged DNA, and helps to maintain normal mitochondrial respiratory function. It is controlled by the fusion proteins, mitofusin 1 (Mfn1) (Santel et al., 2003) and mitofusin 2 (Mfn2) (Santel et al., 2001), which mediate fusion of the OMM between two adjacent mitochondria, and optic atrophy protein 1 (OPA1) (Cipolat et al., 2004; Burke et al., 2015) that executes inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) fusion.
The relevance of mitochondrial dynamics to the adult heart has been confirmed in adult mouse models deficient in the different mitochondrial shaping proteins, in which mitochondrial dysfunction and cardiomyopathies have been shown to develop. Genetic ablation of the mitochondrial fission proteins [Drp1 (Ikeda et al., 2015), MFF (Chen et al., 2015) or mitochondrial fusion proteins (Mfn2 (Papanicolaou et al., 2011), OPA1 (Chen et al., 2012)] have been shown to modify mitochondrial shape and impair mitochondrial respiratory function, and result in the development of cardiomyopathy. An imbalance between mitochondrial fission and fusion in the heart has been shown to contribute to the pathogenesis of a variety of cardiomyopathies including those resulting from diabetes, pressure-overload LVH, and doxorubicin cardiotoxicity, highlighting the important role of mitochondrial shaping proteins in maintaining normal cardiac function, and positioning them as therapeutic targets to improve outcomes in patients with these cardiomyopathies (Ong et al., 2010; 2013; 2015; Hernandez-Resendiz et al., 2020). Targeting mitochondrial shaping proteins has also been shown to be beneficial in a number of other cardiac diseases including acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury, post-ischemic cardiomyopathy and sepsis-related cardiomyopathy, and are reviewed elsewhere (Hernandez-Resendiz et al., 2020; Kalkhoran et al., 2020).
Diabetic cardiomyopathy
The global prevalence of DM has reached epidemic proportions, reaching 9.7% among US adults (Xu et al., 2018). Patients with DM are ~2-5 fold more likely to develop HF (Dei et al., 2015). This has focused research on understanding the mechanisms underlying diabetic cardiomyopathy (DMC) (Rubler et al., 1972), as a distinct cardiac disease entity, and a significant cause of HF in DM patients. DMC has been defined as a clinical condition of left ventricular (LV) dysfunction that occurs in the absence of coronary atherosclerosis, valvular heart disease, and hypertension in patients with DM (Yancy et al., 2017; Cosentino et al., 2020). Currently, there are no well-defined clinical criteria for diagnosing DMC, nor are there specific treatments for preventing DMC, and this may be due, in part, to the lack of understanding of the underlying mechanisms. DMC is a complex entity arising from multiple pathophysiological mechanisms including hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, lipotoxicity, microvascular changes, and inflammation (Dillmann 2019; Cong S et al., 2020). The presence of diabetes is known to impact on the susceptibility of the heart to acute ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI)(Penna et al., 2020). Here, we focus on the role mitochondrial shaping proteins play in contributing to the pathogenesis of DMC, and highlight potential treatment strategies for preventing the onset and progression of DMC (Figure 1).
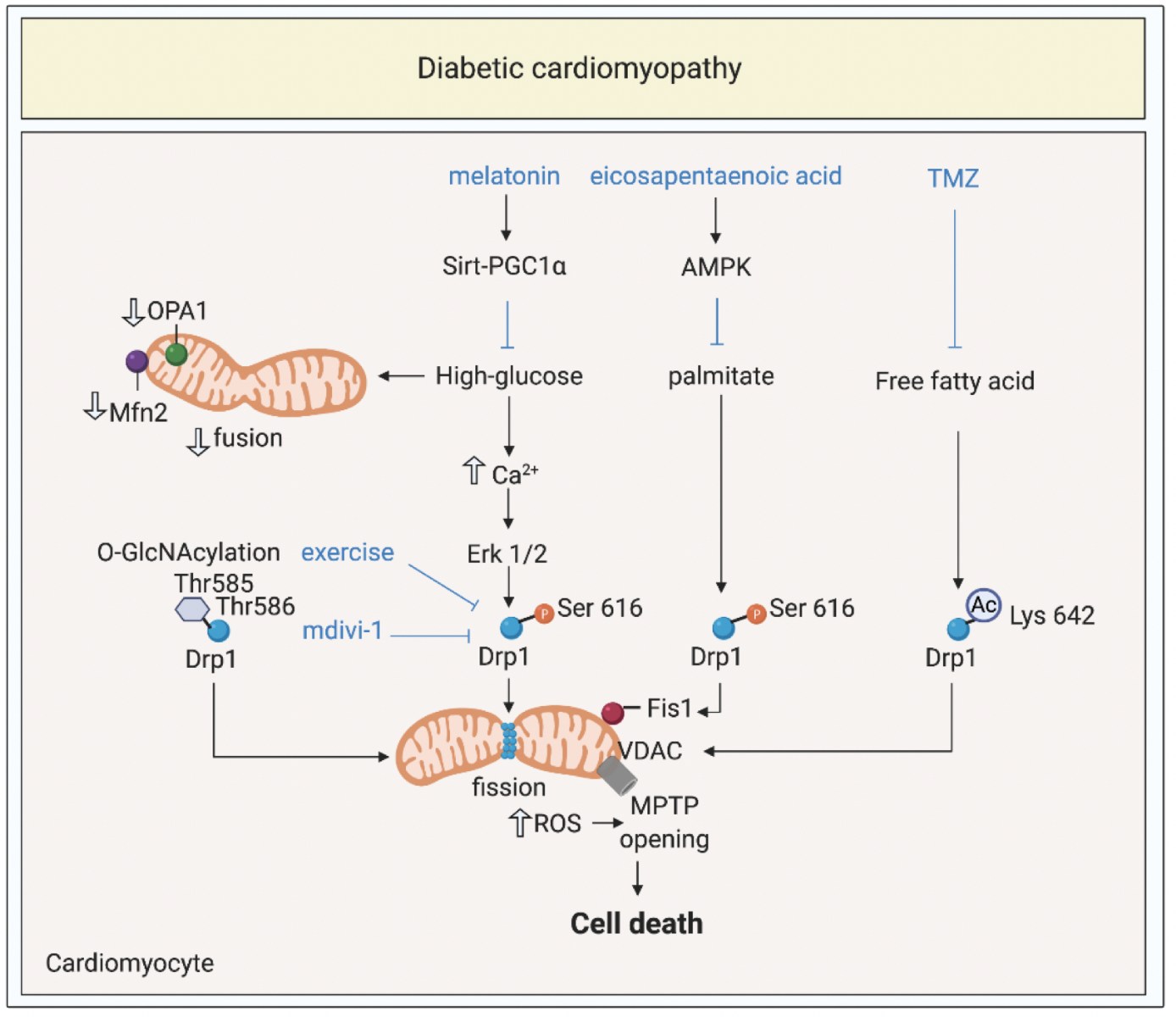
In a new window | Download PPT
Figure 1: Targeting mitochondrial shaping proteins as treatment strategy for diabetic cardiomyopathy. High-glucose and lipotoxicity (from free fatty acids including palmitate) induce activation and mitochondrial translocation of Drp1, suppression of Mfn2 and OPA1, mitochondrial fission, increased ROS production, MPTP opening, and cell death through different signalling pathways. These pathways can be targeted by therapies such as melatonin, eicosapentanenoic acid, Trimetazidine, mdivi-1, and exercise to prevent onset and progression of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Dynamin-related protein 1, Drp1; optic atrophy protein 1, OPA1; mitofusin 2, Mfn2; mitochondrial permeability transition pore, MPTP; trimetazidine, TMZ; O-linked N-acetyl-glucosamine glycosylation, O-GlcNAcylation; reactive oxygen species, ROS; 5’ AMP-activated protein kinase, AMPK; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, PGC1α; voltage dependant anion channels, VDAC; extracellular regulated kinase, Erk.
High-glucose induced mitochondrial fission
Increased levels of mitochondrial oxidative stress are known to contribute to the vascular and multi-organ complications of DM (Nishikawa et al., 2000). Studies in cardiomyocytes have shown that altered mitochondrial dynamics, and resultant mitochondrial oxidative stress occur in response to high-glucose (HG) exposure. In H9c2 rat myoblasts, HG was demonstrated to induce a biphasic change in mitochondrial morphology with Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission, and subsequent mitochondrial oxidative stress occurring at 15 min, and normalizing by 60 min, and a second more sustained phase of fission and oxidative stress, occurring 10 hours later, and normalizing by the 18-hours (Yu et al., 2006). Prolonged exposure (up to 48 hours) to HG has been reported to induce sustained mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress that resulted in the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP), and apoptotic cell death in H9c2 cells (Yu et al., 2008). Together, these studies demonstrate the role of mitochondrial fission in mediating the glucotoxic effects of HG in cardiomyocytes.
The mechanisms through which HG induces mitochondrial fission have been investigated in several studies. HG has been demonstrated in H9c2 cells to induce mitochondrial fission through an increase in cytosolic calcium and phosphorylation of Drp1 at Ser616 by extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (Erk1/2) (a post-translational modification of Drp1, which promotes its mitochondrial translocation) (Gawlowski et al., 2012). Mitochondrial proteins have been shown to be post-translationally modified by O-linked N-acetyl-glucosamine glycosylation (O-GlcNAcylation) in cardiomyocytes exposed to HG, and in the diabetic heart (Hu et al., 2009; Jensen et al., 2019). HG has been shown to induce mitochondrial fission in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes by decreasing OPA1 levels, and increasing O-GlcNAcylation, effects which were reversed by overexpressing OPA1 (Hu et al., 2009). Similarly, HG has been reported to induce mitochondrial fission in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes by enhancing O-GlcNAcylation of Drp1 at Thr585 and Thr586, which decreased phosphorylation of Drp1 at Ser637 (a post-translational modification of Drp1 that prevents its mitochondrial translocation) (Gawlowski et al., 2012). The etiological role of Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission in mediating glucotoxic effects in a diabetic mouse model has been investigated with the genetic expression of the Drp1-K38A dominant-negative mutant, which protected against HG-induced mitochondrial fission, oxidative stress, and diabetic nephropathy, although the effects on the heart were not tested (Galloway et al., 2012). A recent study has also implicated reduction in myocardial levels of Mfn2 as a potential mediator of mitochondrial fragmentation, and development of DMC in a diabetic mouse model. Intramyocardial injection of adenoviral vectors encoding Mfn2 normalized mitochondrial morphology and function, attenuated apoptotic cell death, decreased oxidative stress, and prevented the onset of DMC. This opens up the possibility of using chronic therapy with Mfn2 activating mini-peptides (Franco et al., 2016) or small molecules (Rocha et al., 2018) as a novel treatment strategy for DMC.
Studies have shown that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and ER stress-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis may be triggered by HG, free fatty acids, and inflammation, and contribute to the pathogenesis of DMC (Yang et al., 2015). The mitochondrial fusion protein, Mfn2, has been reported to play an important non-fusion pleiotropic role in acting as a tether between ER and mitochondria (de Brito et al., 2008a), to facilitate calcium signaling between these two organelles. Yang et al (2017) showed in a DM rat and in HG-exposed H9C2 cells, that ER-stress apoptosis markers were increased and MPTP opening was enhanced, and this could be abolished by either long-term administration of exogenous hydrogen sulfide (a known cardioprotective agent) or genetic inhibition of Mfn2, the latter showing that dissociating ER from mitochondria can protect the heart against HG-induced ER-stress and mitochondrial apoptosis signaling (Yang et al., 2017).
Lipotoxicity induced mitochondrial fission
Reduced insulin sensitivity in DM and associated elevations in circulating levels of free fatty acids, have been shown to induce lipotoxic effects in cardiomyocytes including mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and alterations in mitochondrial morphology, and in this way, may contribute to the pathogenesis of DMC. In neonatal rat cardiomyocytes, Kuzmicic et al. (2014) showed that exposure to palmitate increased the localization of Drp1 with Fis1, induced mitochondrial fission, and resulted in apoptotic cell death. It has also been shown that the mitochondrial phospholipid acyltransferase, tafazzin, was upregulated in H9c2 cells exposed to palmitate, and this was shown to be upstream of Drp1-mediated fission (Chang et al., 2019). A high-fat diet in mice and monkeys have been reported to induce obesity and DM, and resulted in increased phosphorylation of Drp1 at Ser616, decreased phosphorylation of Ser637, enhanced mitochondrial translocation of Drp1, and resulted in myocardial injury (Hu et al., 2020). In this study, it was shown that palmitate-induced acetylation of Drp1 at Lys642, which induced its translocation to VDAC1 to mediate mitochondrial fission and MPTP opening, contractile dysfunction, and cardiomyocyte death (Hu et al., 2020). A high-fat diet in mini-pigs has also been reported to alter mitochondrial shaping proteins in the heart, with upregulation of fission proteins and downregulation of fusion proteins, although the effect on mitochondrial morphology was not investigated (Chen et al., 2020). A direct toxic effect of free fatty acids on the heart in terms of inducing mitochondrial fission and cardiac dysfunction in the absence of obesity and DM, has been reported in mice with cardiomyocyte-specific overexpression of fatty acid transport protein 1, (FATP1) (Elezaby et al., 2015). Similarly, transgenic mice overexpressing cardiomyocyte-specific long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 1, demonstrated increased myocardial fatty acid uptake, mitochondrial fission, increased ROS production, and cardiac dysfunction (Tsushima et al., 2018). Exposure of cardiomyocytes to palmitate was shown to increase ubiquitination of A-kinase anchor protein leading to reduced phosphorylation of Drp1 at Ser637, and altered proteolytic processing of OPA1 (Tsushima et al., 2018). Finally, decreasing cardiomyocyte lipolysis by cardiomyocyte-specific overexpression of Perilipin 5 has been reported to preserve cardiac function despite high levels of cardiac fatty acids, and this protective effect was associated with decreased phosphorylation of MFF at Ser146, less mitochondrial Drp1, and inhibition of mitochondrial fission (Kolleritsch et al., 2020).
Mitochondrial fission in the diabetic heart
Altered mitochondrial morphology in terms of small fragmented mitochondria has also been observed in rodent models of DMC, and in heart tissue from DM patients. In the streptozotocin-induced type 1 DM mouse heart, interfibrillar but not subsarcolemmal mitochondria were observed to be smaller when compared to non-DM mice, confirming that mitochondrial morphology was altered in vivo in response to sustained HG conditions (Dabkowski et al., 2009). These changes in the shape of the mitochondria in the DM heart were associated with impaired mitochondrial respiration rates, enhanced oxidative stress, increased susceptibility to MPTP opening, and a propensity to apoptosis when compared to non-DM hearts (Dabkowski et al., 2009; Williamson et al., 2010). Studies of human atrial appendage tissue from DM patients undergoing cardiac bypass surgery have demonstrated the presence of mitochondrial dysfunction (as evidenced by impaired mitochondrial respiration and increased oxidative stress) when compared to non-DM patients (Anderson et al., 2009; Montaigne et al., 2014). Furthermore, atrial appendage tissue from DM patients without overt cardiomyopathy had smaller mitochondria on electron microscopy, and reduced expression of Mfn1 (Montaigne et al., 2014), demonstrating the relevance of altered mitochondrial morphology to the human DM heart.
Mitochondrial fission and cardiac microvascular function
Given the contribution of microvascular disease to the pathogenesis of DMC, the effect of HG and diabetes on endothelial cells has been investigated. Experimental studies have shown that HG induces mitochondrial fission in vitro in endothelial cells (Paltauf-Doburzynska et al., 2004; Shenouda et al., 2011), and in coronary endothelial cells (CECs) (Makino et al., 2010). CECs isolated from DM mice have been shown to have fragmented mitochondria, findings which were associated with increased mitochondrial oxidative stress, reduced levels of OPA1, and increased levels of Drp1, changes which were abrogated by treatment of DM mice with antioxidant therapy (Makino et al., 2010). Similarly, HG was shown to induce mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress in human CECs (Makino et al., 2010). The transient receptor potential channel, subtype melastatin 2 (TRPM2) ion channel has been implicated as a potential novel mediator of HG-induced fission in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and primary mice endothelial cells (Abuarab et al., 2017). It was shown that HG may induce mitochondrial fission through a pathway involving extracellular Ca2+ entry through ROS-activated TRPM2 channels, Ca2+-induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization, redistribution of lysosomal Zn2+ to mitochondria, and Zn2+-induced mitochondrial recruitment of Drp-1 (Abuarab et al., 2017). Large clinical outcome studies have reported that a new group of anti-diabetic agents, sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors such as empagliflozin (Zinman et al., 2015) reduced cardiovascular death and hospitalization for HF in DM patients, although the mechanisms underlying this beneficial effect remain unclear. Zhou et al (2018) have investigated the effects of empagliflozin on coronary microvascular injury in DM and linked its vasculoprotective effects to the inhibition of Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission in CECs. They found that empagliflozin improved myocardial structure and function, preserved cardiac microvascular barrier function and integrity, sustained eNOS phosphorylation, and endothelium-dependent relaxation, as well as improved microvessel density and perfusion (Zhou et al., 2018). Empagliflozin was shown to exert its salutary effects through suppression of mitochondrial oxidative stress and inhibition of mitochondrial fission in an adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent manner involving suppressed Drp1 Ser616 phosphorylation, and increased Drp1 Ser637 phosphorylation (Zhou et al., 2018). Similar beneficial effects in terms of the inhibition of mitochondrial fission and preservation of function have been observed in DM CECs with the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, vildagliptin, another new anti-diabetic class of agents (Liu et al., 2019).
Therapeutic targeting of mitochondrial shaping proteins to prevent DMC
Prior studies have shown that acute inhibition of IRI-induced mitochondrial fission with a one-off application of mdivi-1 (a pharmacological inhibitor of Drp1) at the time of reperfusion in the DM heart, reduced MI size, demonstrating IRI-induced fission as a target for acute cardioprotection (Ding et al., 2017). Several studies have investigated whether chronic modulation of the mitochondrial shaping proteins can delay the onset of and progression of DMC in animal DM models. Veeranki et al (2016) found in DM mice that moderate intensity exercise (5 weeks of treadmill exercise) improved cardiac function, reduced myocardial fibrosis, restored interstitial and micro-vessels associated Cx43 levels, increased gap junction intercellular communication, improved mitochondrial respiration rates and ATP levels, and attenuated myocardial Drp1 levels, although the effects of exercise on mitochondrial morphology were not directly tested. These data highlight the potential for exercise as a strategy for preventing diabetic cardiomyopathy (Crisafulli et al., 2020). Ding et al (2018) have shown that chronic therapy with melatonin over a period of 10 weeks was able to prevent the onset of DMC, and inhibited mitochondrial fission in DM wild-type mice but not mice deficient in cardiac sirtuin 1 (Sirt1). In vitro studies in H9C2 cells showed that melatonin inhibited HG-induced mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress through a Sirt1- peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC1α) pathway (Ding et al., 2018). Interestingly, in the same study, it was shown that chronic therapy with the Drp1 inhibitor, mdivi-1, over a period of 10 weeks was able to inhibit mitochondrial fission, attenuate apoptotic cell death, preserve mitochondrial respiratory function, and improve cardiac function in DM mice (Ding et al., 2018). These findings may potentially allay concerns over the detrimental effects observed with chronic genetic ablation of Drp1 in terms of a cardiomyopathy arising from impaired mitophagy and the accumulation of damaged mitochondria (Ikeda et al., 2015). The SGLT2 inhibitor, empagliflozin, has also been reported to protect the DM rat heart following AMI, as evidenced by less IRI-induced mitochondrial fission, attenuated oxidative stress and enhanced mitophagy, although the effect on MI size and the development of DMC was not evaluated (Mizuno et al., 2018). Furthermore, the mechanisms through which SGLT inhibitors would modulate mitochondrial morphology is not clear given that SGLT2 receptors have not been found in cardiomyocytes(Chen et al., 2010). Finally, Ding et al (Ding et al., 2020) demonstrated in a DM rat model that chronic therapy for 6 weeks with the mitochondrial fusion promoter, M1, promoted mitochondrial fusion and attenuated the decline in OPA1 expression observed in DM hearts, and decreased oxidative stress, improved mitochondrial respiratory function, and prevented the onset of DMC in DM rats, highlighting an alternative approach to preventing mitochondrial fission in the DM heart.
Trimetazidine (TMZ), an antianginal drug used in Europe and Asia that has been proposed as a metabolic modulator for HF treatment, is known to decrease free fatty acid oxidation, and has been shown in neonatal cardiomyocytes to induce mitochondrial fusion at baseline, and inhibit palmitate-induced mitochondrial fission and preserve mitochondrial respiratory function (Kuzmicic et al., 2014). The N3-polyunsaturated fatty acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, which has been reported to have beneficial effects against cardiovascular diseases, has been shown to inhibit palmitate-induced mitochondrial Drp1 expression and fission in H9c2 cells through the activation of AMPK (Sakamoto et al., 2017). These two studies provide examples of drug repurposing and potential therapeutic strategies for preventing the lipotoxicity associated with DMC. Maneechote et al. (2019) have investigated the beneficial effects of targeting the mitochondrial shaping proteins as a treatment strategy for protecting against lipotoxicity. They found that a high-fat diet in rats resulted in obesity and insulin resistance, induced mitochondrial fission, imbalanced mitochondrial shaping proteins, caused mitochondrial dysfunction, increased apoptosis, and induced cardiac dysfunction (Maneechote et al., 2019). These detrimental effects were normalized by treating rats with mdivi-1 (the small molecule inhibitor of Drp1), and M1 (the small molecule fusion promoter) for 2 weeks, and the ameliorating effects of these agents were additive, providing a combination treatment strategy for preventing lipotoxicity in the heart (Maneechote et al., 2019).
In summary, excessive mitochondrial fission and resultant mitochondrial oxidative stress and increased propensity to apoptotic cell death, have been shown to contribute to the pathogenesis of DMC, raising the possibility of targeting mitochondrial shaping proteins to normalize mitochondrial morphology as a therapeutic strategy for preventing the onset and progression of DMC (Figure 1).
Pressure-overload left ventricular hypertrophy and cardiomyopathy
Hypertension and valvular heart disease are significant causes of HF worldwide. They are characterized by increased pressure overload on the heart, which results in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), myocardial fibrosis, cardiomyocyte death, and can culminate in HF if the sustained overload is maintained. Again, mitochondrial dysfunction and disturbances in mitochondrial morphology have been shown to contribute to the pathogenesis of pressure-overload cardiomyopathy (Figure 2).
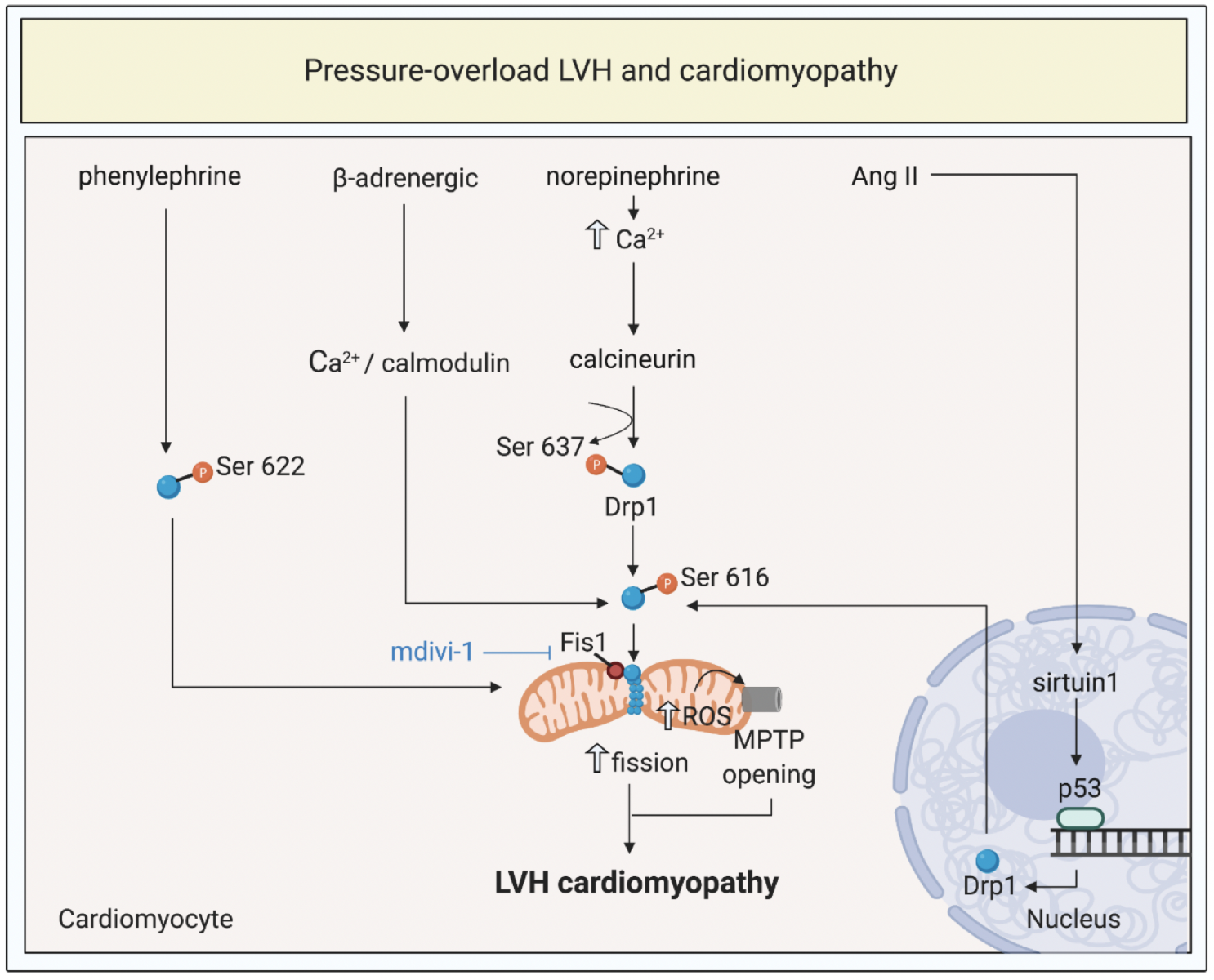
In a new window | Download PPT
Figure 2: Targeting mitochondrial shaping proteins as a treatment strategy for pressure-overload left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and cardiomyopathy. Pressure-overload LVH by total aortic constriction induce activation and mitochondrial translocation of Drp1, mitochondrial fission, increased ROS production, and MPTP opening through different signalling pathways. These pathways can be targeted by therapies such as mdivi-1 to prevent onset and progression of LVH and cardiomyopathy.
Dynamin-related protein 1, Drp1; fission protein 1, Fis1; mitochondrial permeability transition pore, MPTP; reactive oxygen species, ROS; angiotensin II, Ang II.
Mitochondrial fission and pressure-overload LVH and cardiomyopathy
In neonatal rat cardiomyocytes, Pennanen et al. (2014) demonstrated that the hypertrophic agonist, norepinephrine, induced mitochondrial fission and dysfunction, through the activation of α1-adrenergic receptors and increased cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels, which in turn activates calcineurin that dephosphorylates Drp1 at Ser637 to promote mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. The effects of norepinephrine on cellular hypertrophy and mitochondrial fission were abrogated by the dominant-negative Drp1 (K38A) mutant (Pennanen et al., 2014). Interestingly, in the same study, genetic ablation of Mfn2 also induced mitochondrial fission and stimulated a cellular hypertrophic response, demonstrating the importance of altered mitochondrial dynamics in the cellular hypertrophic response (Pennanen et al., 2014). Consistent with this role of Mfn2 in protecting against LVH, prior studies have shown that mouse hearts deficient in Mfn2 developed LVH and subsequent cardiomyopathy (Papanicolaou et al., 2011), the reasons for which are not clear, but may relate to its non-fusion effects on inhibiting and acting as a tether between sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) and mitochondria for calcium signaling (de Brito et al., 2008b; de Brito et al., 2008a). In the pressure-overload total aortic constriction (TAC) LVH model, dynamic changes in mitochondrial morphology have been observed with transient elongation of mitochondria 24 hours after TAC, followed by fragmentation 3 to 5 days after TAC, and then re-elongation of mitochondria 30 days after TAC, and these changes were accompanied by the expected correlations in Ser637 and Ser616 phosphorylation of Drp1 (Shirakabe et al., 2016).
Therapeutic targeting of mitochondrial shaping proteins to prevent LVH and cardiomyopathy
Early studies have reported that treatment with mdivi-1 for one week prevented cardiac dysfunction in a mouse TAC model of LVH (Givvimani et al., 2012). Subsequently, Chang et al (2013) showed phosphorylation of Drp1 at Ser622, and mitochondrial translocation of Drp1, in an acute pressure overload and chronic LVH TAC mouse model, and phenylephrine-treated cardiomyocytes. Chronic therapy with mdivi-1 over 2 weeks prevented these changes, and reduced the onset of LVH in this model (Chang et al., 2013). However, neither of these two studies investigated the direct effect of TAC on mitochondrial morphology. LVH induced by chronic β-adrenergic receptor agonist has been reported to be due to the activation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II, phosphorylation of Drp1 at Ser616, mitochondrial translocation of Drp1, and mitochondrial fission, which in turn resulted in MPTP opening, impaired mitochondrial respiratory function, and cardiac dysfunction (Xu et al., 2016). Genetic ablation of Drp1 or treatment with mdivi-1 was shown to attenuate mitochondrial fission and prevent LVH in this mouse model of chronic β1-adrenergic receptor (β1-AR) stimulation (Xu et al., 2016). Finally, Qi et al. (2018) reported that angiotensin II (AgII)-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis was induced via a Sirt1-p53-Drp1 pathway involving mitochondrial fission. Chronic treatment of spontaneously hypertensive rats with mdivi-1 to inhibit Drp1 was shown to prevent AgII-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis, attenuate LVH, and preserve cardiac function (Qi et al., 2018). These three studies provide evidence for Drp1 as a therapeutic target for preventing the onset of cardiomyopathy associated with LVH. Although chronic pharmacological inhibition of Drp1 has been shown to protect against LVH and cardiomyopathy, genetic ablation of Drp1 has been shown to worsen LVH and induce cardiac dysfunction in mice following TAC, an effect most likely attributed to impaired mitophagy and accumulation of damaged mitochondria (Shirakabe et al., 2016).
In summary, excessive mitochondrial fission and resultant mitochondrial dysfunction, have been shown to contribute to the pathogenesis of pressure-overload cardiomyopathy, providing the opportunity to target mitochondrial shaping proteins to normalize mitochondrial morphology as a therapeutic strategy for preventing the onset and progression of pressure-overload cardiomyopathy (Figure 2).
Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity
The anthracycline antibiotic, doxorubicin is a highly effective chemotherapeutic agent for treating lymphomas and breast cancer, but its use has been limited by its cardiotoxic effects, which can result in cardiomyopathy in about 9% of patients depending on the dose used (Cardinale et al., 2015). The mechanisms underlying doxorubicin cardiotoxicity are unclear, although two main mechanisms have been proposed. The first is based on oxidative stress, which in the presence of iron, generates reactive oxygen species that cause lipid peroxidation of the cell membrane leading to cardiomyocyte injury. The second one proposes that inhibition of topoisomerase IIβ results in the activation of cell death pathways and inhibition of mitochondrial biogenesis (reviewed in (Saleh et al., 2020)). In both these mechanisms, mitochondrial dysfunction has been shown to play a key role in the pathogenesis of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity, and in this respect, emerging data has implicated a role for altered mitochondrial morphology as an etiological factor (Figure 3).
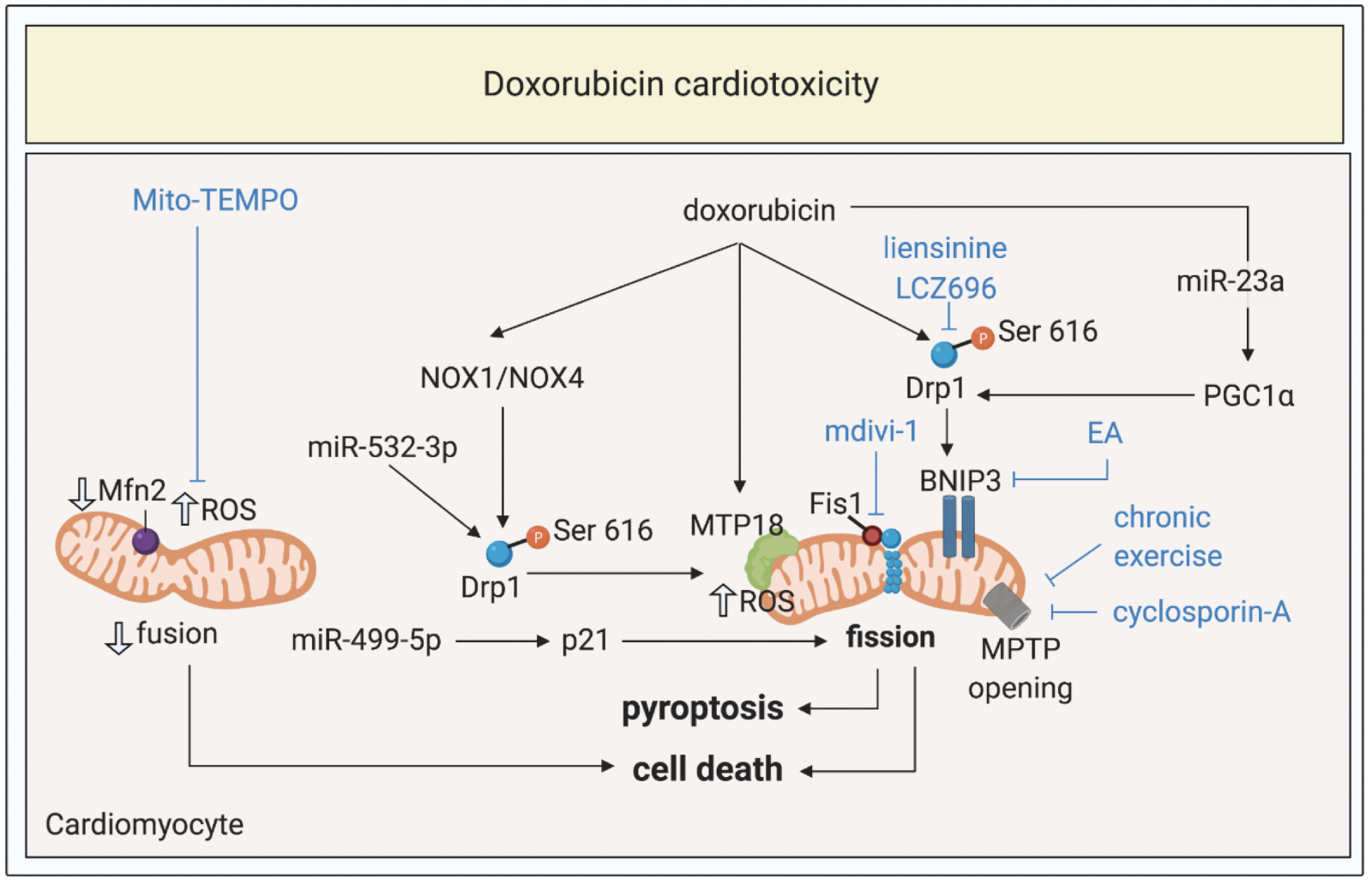
In a new window | Download PPT
Figure 3: Targeting mitochondrial shaping proteins as treatment strategy for doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Doxorubicin induces activation and mitochondrial translocation of Drp1, reduction of Mfn2, mitochondrial fission, increased ROS production, MPTP opening, pyroptosis, and cell death through different signalling pathways. These pathways can be targeted by therapies such as liensinine, LCZ696, exercise, cyclosporine-A, mdivi-1, Mito-TEMPO to protect against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity.
Dynamin-related protein 1, Drp1; optic atrophy protein 1, Mfn2; mitochondrial permeability transition pore, MPTP; ellagic acid, EA; reactive oxygen species, ROS; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, PGC1α; NADPH oxidase 1 and 4; NOX1 and NOX4.
Doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial fission
The first study to show altered mitochondrial morphology in cardiomyocytes exposed to doxorubicin was by Parra et al. (2008), who demonstrated fragmentation of the mitochondrial network in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes after 24 hours incubation with doxorubicin. A recent study in neonatal cardiomyocytes has shown that doxorubicin induces the activation of the hypoxia-inducible death protein, Bcl-2 nineteen-kilodalton interacting protein 2 (BNIP3) (that mediates cell death via localizing to mitochondria), and this was associated with the phosphorylation of Drp1 at Ser616, resulting in mitochondrial fission, oxidative stress, MPTP opening, and cell death (Dhingra et al., 2017). Studies have confirmed the presence of fragmented mitochondria in mice models of acute and chronic doxorubicin cardiotoxicity (Marechal et al., 2011). Mice deficient in Drp1 (heterozygous Drp1+/-) have been shown to be protected against doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial fission, mitophagy, and cardiomyopathy, confirming the role of Drp1 as a mediator of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity (Catanzaro et al., 2019). Interestingly, pharmacological inhibition of the MPTP using cyclosporin-A has been shown in this animal model to inhibit mitochondrial fission, suppress MPTP opening, and prevent cardiac dysfunction following doxorubicin exposure, suggesting that MPTP opening is upstream of mitochondrial fission in this setting (Marechal et al., 2011). The novel mitochondrial fission protein, MTP18, has been reported to contribute to doxorubicin-mediated Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission in HL-1 cardiomyocytes (Aung et al., 2017). Interestingly, doxorubicin has been shown to reduce myocardial levels of forkhead box class O 3a (Foxo3a), which in turn resulted in increased expression of the mitochondrial fission protein, MiD49, inducing mitochondrial fission and cardiac dysfunction, effects which were abolished by genetic overexpression of Foxo4 or by genetic ablation of MiD49 (Zhou et al., 2017). Finally, the mitochondrial fusion protein, Mfn2, has also been implicated in doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial fission, with doxorubicin exposure reducing Mfn2 levels and resulting in mitochondrial fission, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes, detrimental effects that were abrogated by either Mfn2 over-expression or the anti-oxidant agent, Mito-TEMPO (Tang et al., 2017).
The mechanisms through which doxorubicin induces mitochondrial fission in cardiomyocytes are not clear. In neonatal cardiomyocytes, Samant et al. (2014) linked the effect to the acetylation of OPA1, which reduced the latter’s activity, the expected result of which would be to induce mitochondrial fission. This mechanistic pathway was supported by data showing that adenoviral transfection of Sirt3, which is known to deacetylate OPA1, increased OPA1 activity, and restored the mitochondrial network (Samant et al., 2014). Several miRNAs have been investigated as potential therapeutic targets for inhibiting mitochondrial fission and preventing doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Wang et al. (2015) have shown that doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial fission, was mediated by a pathway involving the miR-532-3p-mediated suppression of apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain (ARC), highlighting the possibility of using an antagomir to miR-532-3p as a potential therapeutic intervention to protect against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Similarly, the miR-499-5p-p21 axis was shown to protect against doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial fission, apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction in a mouse model (Wan et al., 2018). Finally, doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial fission has been linked to the activation of a miR-23a-PGC-1α/p-Drp1 pathway positioning miR-23a as a therapeutic target for preventing doxorubicin cardiotoxicity (Du et al., 2019). An interesting recent study has investigated the role of mitochondrial fission and pyroptosis (NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated cell death) in doxorubicin-cardiotoxicity, showing that doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial fission was mediated via NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1)/NOX4 phosphorylation of Ser616 and dephosphorylation of Ser637 of Drp1, which resulted in pyroptotic cell death (Zeng et al., 2020).
Therapeutic targeting of mitochondrial shaping proteins to prevent doxorubicin cardiotoxicity
The first experimental study to investigate the targeting of mitochondrial shaping proteins as a treatment strategy for preventing doxorubicin cardiotoxicity was by Ghanarei et al. (2013), who demonstrated in the isolated perfused rat heart that perfusion with the Drp1 inhibitor, mdivi-1, activated the cytoprotective pro-survival kinases, Akt and Erk1/2, and prevented cardiac dysfunction. In isolated cardiomyocytes, mdivi-1 was shown to inhibit MPTP opening, placing mitochondrial fission upstream of MPTP opening (Gharanei et al., 2013). Importantly, in this study, co-incubation of mdivi-1 with doxorubicin did not alter the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin against leukemic HL60 cells, showing that this therapeutic approach did not interfere with the chemotherapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin (Gharanei et al., 2013). However, this study only investigated short-term inhibition of mitochondrial fission in an ex vivo heart perfusion model.
A number of therapeutics have been investigated for their ability to protect the heart against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity through the inhibition of mitochondrial fission. Ellagic acid (EA), a naturally occurring compound, found in fruits, vegetables, and berries was shown to inhibit doxorubicin-induced activation of BNIP3, and through this action, it prevented mitochondrial fission, MPTP opening, and cell death in neonatal cardiomyocytes (Dhingra et al., 2017). The mitophagy inhibitor, liensinine (a plant-derived isoquinoline alkaloid), has been shown to decrease Drp1 phosphorylation at Ser616 site, inhibit mitochondrial fission, lessen mitophagy, attenuate oxidative stress, and attenuate cardiomyocyte apoptosis, thereby improving mitochondrial function and preserving cardiac contractile function in a doxorubicin animal model (Liang et al., 2020). Drug repurposing may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for inhibiting mitochondrial fission to prevent doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. In this regard, it has been shown that, LCZ696, a novel angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor, that has been used to treat HF, abrogated doxorubicin-induced phosphorylation of Ser616 of Drp1, mitochondrial fission, and preserved mitochondrial respiratory function in mice treated with doxorubicin (Xia et al., 2017). Chronic exercise has been reported in a rat model to normalize the effects of doxorubicin on MPTP opening susceptibility and expression of mitochondrial shaping proteins, although the direct effects of exercise mitochondrial morphology were not studied (Marques-Aleixo et al., 2018).
In summary, excessive mitochondrial fission and resultant mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy, have been shown to contribute to the pathogenesis of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity, raising the possibility of targeting mitochondrial shaping proteins to normalize mitochondrial morphology as a therapeutic strategy for preventing the onset and progression of anthracycline cardiomyopathy (Figure 3). However, when testing new cardioprotective therapies directed to the mitochondrial shaping proteins, it is important to test that they do not interfere with the chemotherapeutic effect of anthracyclines.
Summary, therapeutic challenges, and future perspectives
Imbalances in mitochondrial fission and fusion in the heart with excess fission have been shown to result in mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction, and contribute to the pathogenesis of cardiomyopathies secondary to diabetes, pressure-overload, and doxorubicin cardiotoxicity, positioning the mitochondrial shaping proteins as therapeutic targets for preventing the onset and progression of HF (Kalkhoran et al., 2020). However, chronic pharmacological inhibition of mitochondrial fission as a treatment strategy for preventing cardiomyopathy in these settings may be challenging for several reasons: (1) Chronic genetic inhibition of Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission has been shown to inhibit mitophagy resulting in the accumulation of damaged mitochondria and the development of cardiomyopathy (Ikeda et al., 2015), although several studies have shown that chronic pharmacological inhibition of Drp1 using mdivi-1 prevented DMC (Ding et al., 2018) and cardiac lipotoxicity (Maneechote et al., 2019) with no obvious adverse effects; (2) Given the ubiquitous and critical roles that mitochondrial shaping proteins play in virtually all cells in the body, strategies are needed to target mitochondrial therapeutics to the heart in order to avoid off-target effects - this may be achieved through the use of nanoparticles (Rana et al., 2015; Ishikita et al., 2016; Ong et al., 2017). In this regard, cardiac-targeting nanoparticles have been used to target the delivery of siRNA to p53 to cardiomyocytes in order to prevent the development of LVH and reduce the risk of off-target effects (Rana et al., 2015); (3) Current pharmacological inhibitors of mitochondrial fission proteins such as the small molecule Drp1 inhibitor, mdivi-1 (Cassidy-Stone et al., 2008), have off-target mitochondrial effects (Bordt et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2017), and novel more specific Drp1 inhibitors are needed to translate this therapeutic strategy as a treatment for cardiomyopathy (Numadate et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2020).
In summary, although mitochondrial shaping proteins appear to be attractive therapeutic targets for preventing the onset and progression of DMC, pressure-overload cardiomyopathy, and doxorubicin cardiotoxicity, further studies are needed to overcome the aforementioned challenges, before the targeting of mitochondrial shaping proteins as a therapeutic strategy can be shown to preventing the onset and progression of HF.
Acknowledgement
Sang-Ging Ong is supported by National Institutes of Health grantR00 HL130416 and R01 HL148756. Chrishan Ramachandra is supported by the Singapore Ministry of Health’s National Medical Research Council under its Open Fund-Young Individual Research Grant (NMRC/OFYIRG/0073/2018), the National Health Innovation Centre Singapore under its Innovation to Develop Grant (NHIC-I2S-1811007) and the SingHealth Duke-NUS Academic Medical Centre under its SingHealth Duke-NUS Academic Medicine Research Grant (AM/TP033/2020 [SRDUKAMR2033]). Sauri Hernandez-Resendiz is supported by the Singapore Ministry of Health’s National Medical Research Council under its Open Fund-Young Individual Research Grant (OF-YIRG)–[NMRC/OFYIRG/0078/2018]. Derek Hausenloy is supported by the British Heart Foundation (CS/14/3/31002), the National Institute for Health Research University College London Hospitals Biomedical Research Centre, Duke-National University Singapore Medical School, Singapore Ministry of Health’s National Medical Research Council under its Clinician Scientist-Senior Investigator scheme (NMRC/CSA-SI/0011/2017) and Collaborative Centre Grant scheme (NMRC/CGAug16C006), and the Singapore Ministry of Education Academic Research Fund Tier 2 (MOE2016-T2-2-021). This article is based upon work from COST Action EU-CARDIOPROTECTION CA16225 supported by COST (European Cooperation in Science and Technology).
References
Siavash Beikoghli Kalkhoran1,2,3
1The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute, Institute of Cardiovascular Science, University College London, UK. 2Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disorder Programme, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore. 3National Heart Research Institute Singapore, National Heart Centre, Singapore.
Sauri Hernandez-Resendiz2,3,4
2Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disorder Programme, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore. 3National Heart Research Institute Singapore, National Heart Centre, Singapore. 4Tecnologico de Monterrey, Centro de Biotecnologia-FEMSA, Nuevo Leon, Mexico.
Sang-Ging Ong5,6
5Department of Pharmacology, University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois, United States of America. 6Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois, United States of America.
Chrishan J.A. Ramachandra2,3
2Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disorder Programme, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore. 3National Heart Research Institute Singapore, National Heart Centre, Singapore.
Derek J. Hausenloy1,2,3,7,8
1The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute, Institute of Cardiovascular Science, University College London, UK. 2Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disorder Programme, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore. 3National Heart Research Institute Singapore, National Heart Centre, Singapore. 7Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University Singapore, Singapore. 8Cardiovascular Research Center, College of Medical and Health Sciences, Asia University, Taiwan.
Corresponding author:
Derek J. Hausenloy
Email: derek.hausenloy@duke-nus.edu.sg

In a new window | Download PPT
Figure 1: Targeting mitochondrial shaping proteins as treatment strategy for diabetic cardiomyopathy. High-glucose and lipotoxicity (from free fatty acids including palmitate) induce activation and mitochondrial translocation of Drp1, suppression of Mfn2 and OPA1, mitochondrial fission, increased ROS production, MPTP opening, and cell death through different signalling pathways. These pathways can be targeted by therapies such as melatonin, eicosapentanenoic acid, Trimetazidine, mdivi-1, and exercise to prevent onset and progression of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Dynamin-related protein 1, Drp1; optic atrophy protein 1, OPA1; mitofusin 2, Mfn2; mitochondrial permeability transition pore, MPTP; trimetazidine, TMZ; O-linked N-acetyl-glucosamine glycosylation, O-GlcNAcylation; reactive oxygen species, ROS; 5’ AMP-activated protein kinase, AMPK; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, PGC1α; voltage dependant anion channels, VDAC; extracellular regulated kinase, Erk.

In a new window | Download PPT
Figure 2: Targeting mitochondrial shaping proteins as a treatment strategy for pressure-overload left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and cardiomyopathy. Pressure-overload LVH by total aortic constriction induce activation and mitochondrial translocation of Drp1, mitochondrial fission, increased ROS production, and MPTP opening through different signalling pathways. These pathways can be targeted by therapies such as mdivi-1 to prevent onset and progression of LVH and cardiomyopathy.
Dynamin-related protein 1, Drp1; fission protein 1, Fis1; mitochondrial permeability transition pore, MPTP; reactive oxygen species, ROS; angiotensin II, Ang II.

In a new window | Download PPT
Figure 3: Targeting mitochondrial shaping proteins as treatment strategy for doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Doxorubicin induces activation and mitochondrial translocation of Drp1, reduction of Mfn2, mitochondrial fission, increased ROS production, MPTP opening, pyroptosis, and cell death through different signalling pathways. These pathways can be targeted by therapies such as liensinine, LCZ696, exercise, cyclosporine-A, mdivi-1, Mito-TEMPO to protect against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity.
Dynamin-related protein 1, Drp1; optic atrophy protein 1, Mfn2; mitochondrial permeability transition pore, MPTP; ellagic acid, EA; reactive oxygen species, ROS; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, PGC1α; NADPH oxidase 1 and 4; NOX1 and NOX4.
Supporting Information
Metrics
| Full-Text | Supporting Information | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 11501 | 31 | 0 |
Copyright © 2017 Conditioning Medicine, All Rights Reserved.
Address: Conditioning Medicine Editorial Office, 3500 Terrace Street, Pittsburgh, PA, 15213, USA